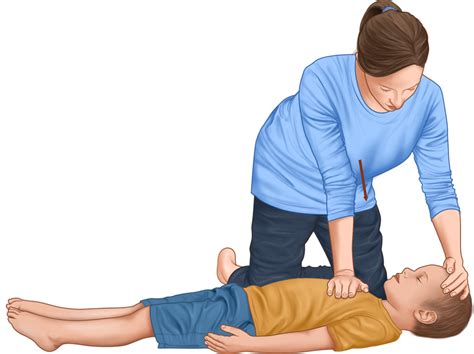
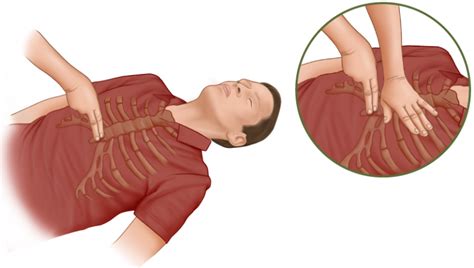
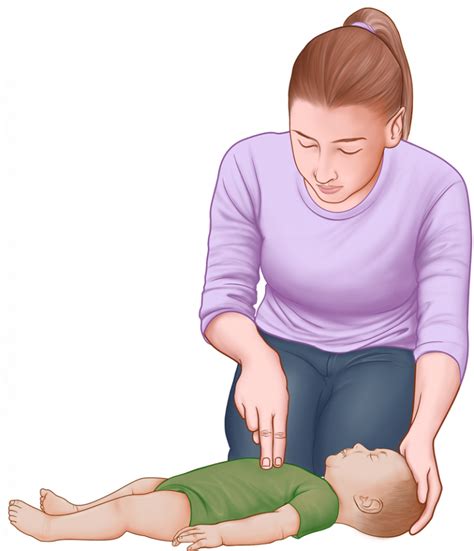
Complete recoil of the chest wall between chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation is recommended, because incomplete chest wall recoil from leaning may decrease venous return and thereby decrease blood flow.
Why is allowing complete chest recoil important when performing CPR quizlet?
Why is allowing complete chest recoil important when performing CPR? The heart will adequately refill between compressions (Allowing complete chest recoil (between compressions) permits blood to flow into the heart. Incomplete chest recoil is inefficient because it reduces the blood flow created by chest compressions.)
Is it important to have both effective chest relaxation recoil and chest compression when performing external CPR?
Allow the chest to recoil completely after each compression, and allow approximately equal compression and relaxation times. Complete chest recoil allows venous return to the heart and is necessary for effective CPR. Studies in people have identified ineffective chest compressions in up to 40% of chest compressions.
What does chest recoil mean allowing time for?
Full chest recoil means allowing the chest to return to normal position after chest compressions. It’s practical to allow for full chest recoil to increase venous return because leaning on the chest prevents the heart from filling with blood. Interruptions.
How can rescuers ensure complete chest recoil during CPR?
Not leaning on the chest between compressions will in turn allow for complete recoil of the chest during CPR. Allowing complete recoil means allowing the sternum to return to its natural state.
Why is allowing complete chest recoil important when performing high quality CPR choose the correct option and select submit?
Chest recoil allows the chest to expand fully or to return to its normal position after chest compressions. Complete chest recoil creates negative pressure that draws blood fully into the heart. This ensures that the perfusion of tissue will be achieved during CPR.
When the person giving chest compressions is not allowing complete chest recoil?
If the person giving chest compressions is not allowing for complete chest recoil, tell the compressor you notice decreased chest recoil—Constructive Intervention.
Why is it important to start chest compression as quickly as possible if someone is unresponsive and not breathing?
However, giving chest compressions is the most important thing to do because their blood already has some oxygen in it and the compressions will keep that blood pumping around their body, taking oxygen to their brain.
Is it acceptable to just perform chest compression only if you are unable or not trained to deliver rescue breaths?
Chest compressions are the priority in CPR. If you can’t to do rescue breathing (mouth-to-mouth) chest compressions alone may still be life-saving. Try to minimise interruptions to chest compressions until help arrives. CPR is a life-saving skill that everyone should learn.
Why is it important not to interrupt chest compressions?
During CPR chest compressions are interrupted for various reasons including rescue breaths, rhythm analysis, pulse-checks and defibrillation. These interruptions decrease coronary and cerebral blood flow and have been associated with decreased survival both in animals and humans (2-4).
Why is it important to not allow more than 10 seconds in between chest compressions?
The number of people who survive rises significantly if the pause is less than 10 seconds. “If your pre-shock pause is over 20 seconds, the chances of surviving to reach a hospital, be treated and be discharged are 53 per cent less than if the pause is less than 10 seconds.” said Dr.
Why is it important to allow the chest to fall between ventilations?
After each compression, allow the chest to recoil completely. Incomplete recoil results in worse hemodynamics, including decreased cardiac perfusion, cerebral perfusion and cardiac output [23].
Why is it important to alternate doing chest compressions?
It seems reasonable to alternate chest compression providers every 2 min, to prevent the loss of effective compressions due to fatigue and to minimise interruptions of chest compressions. The ideal time to do this would be during the rhythm and pulse check as dictated by current guidelines.
What is chest recoil and how do you ensure you are allowing for chest recoil?
But what is chest recoil? This is the concept of taking all of one’s weight off of the chest between each compression to allow the chest to fully expand, which creates a negative pressure that draws blood back into the heart. Drawing blood back into the heart is the only way tissue perfusion is actually able to occur.
Which technique best describes a way you can allow the chest to recoil completely after each chest compression?
Which of the following describes a way you can allow the chest to recoil (allow the heart to completely refill before the next compression) after each chest compression? Take your weight off your hands and allow the chest to come back to its normal position.
How can you ensure chest compressions will be as effective as possible?
You can achieve a high chest compression fraction by compressing the victim’s chest at a rate of 100–120 compressions per minute to a depth of 2–2.4 inches. Avoiding leaning on the chest to allow for full chest wall recoil after each compression and minimize pauses in compressions.
How can rescuer ensure that the rescue breaths are reaching victim’s lungs?
Blow steadily for about one second, watching for the chest to rise. After each breath watch for their chest to fall. Listen and feel for signs that air is being expelled. Maintain the chin lift and tilt position – take another breath and repeat.
Related Article
- Why Fit In When You Are Born To Stand Out?
- Why Don’t I Have The Eye Icon On Tiktok?
- Why Don’t I Have Instagram Notes On My Main Account?
- Why Does The Food In My Fridge Taste Like Chemicals?
- Why Does My Thermostat Setting Not Match My Home’S Temperature?
- Why Does My Phone Automatically Hang Up After 8 Hours?
- Why Does My Ooze Pen Keep Blinking Green After Charging?
- Why Does My Head Itch When I Wear A Hat?
- Why Does My Cat Tap Me When I’M Sleeping?
- Why Does My Body Feel Heavy When I Lay Down?