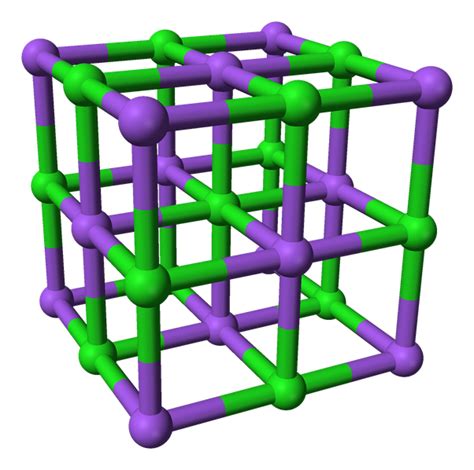
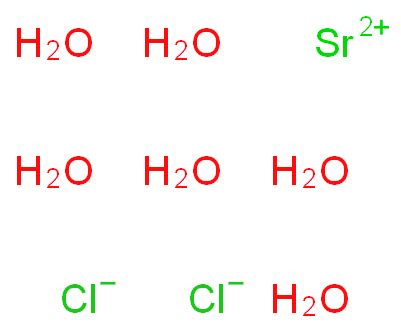
The structure of strontium chloride is similar to that of fluorite. It forms a crystalline solid. In the gaseous phase, the SrCl2 molecule is non-linear and has an angle of around 130° between the Cl-Sr-Cl atoms. This is an anomaly to the VSEPR theory, which suggests a linear structure.
What is an extended structure?
An extended structure is a pattern of subunits that occur in a constant ratio and are arranged in a repeating pattern. These subunits can be individual atoms or molecules, and the composition of the structure is determined by the ratio of elements that make it up. Unlike other structures, extended structures do not have a specific composition, but rather a consistent arrangement of subunits. This unique characteristic makes extended structures important in various fields, including materials science, chemistry, and physics.
Understanding the properties and behavior of extended structures can lead to the development of new materials and technologies.
What is the difference between an extended structure and a molecule?
The makeup of a molecule is determined by the number and type of atoms it contains. For instance, a water molecule is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. On the other hand, the composition of an extended structure, such as table salt, is defined by the ratio of elements that make it up. In the case of table salt, there is a one-to-one ratio of sodium and chlorine atoms.
Understanding the composition of molecules and extended structures is crucial in fields such as chemistry and materials science.
What is an example of an extended structure?
There are various examples of extended structures and molecular-level models that can help us understand the world around us. For instance, sodium chloride and diamonds are examples of extended structures that have unique properties and characteristics. On the other hand, molecular-level models such as drawings, 3D ball and stick structures, and computer representations can help us visualize different molecules with different types of atoms. These models are essential in fields such as chemistry, biology, and physics, as they allow us to study and analyze the behavior of matter at different levels of complexity.
What makes an extended structure an extended structure?
An extended structure is characterized by its size and complexity, as it consists of multiple interconnected components that work together to perform a specific function. These structures can be found in various biological systems, such as the human body, where organs, tissues, and cells form a complex network that enables life-sustaining processes. In materials science, extended structures refer to materials that have a repeating pattern of atoms or molecules, such as crystals or polymers. The key feature of an extended structure is its ability to exhibit emergent properties, which are properties that arise from the interactions between its components and cannot be predicted from the properties of individual components alone.
This emergent behavior is what makes extended structures so fascinating and useful in various fields, from biology to engineering.
Are all solids extended structures?
When we talk about solids, we are referring to a specific type of matter that is defined by its three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules. Unlike liquids or gases, the components of a solid are typically locked into place, creating a stable and rigid structure. This unique property of solids makes them useful in a wide range of applications, from building materials to electronics. Understanding the characteristics of solids is essential for scientists and engineers who work with these materials on a regular basis.
What are examples of extended structures with two kinds of atoms?
Let’s shift our focus to the benefits of meditation for stress relief. If you’re an adult experiencing high levels of stress in your daily life, meditation can be a game-changer. Scientific research has shown that regular meditation practice can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being. One study found that mindfulness meditation can decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression, while another study showed that meditation can lower cortisol levels, the hormone associated with stress.
By taking just a few minutes each day to meditate, you can cultivate a sense of calm and inner peace that can help you better manage stress and improve your quality of life.
Do metals have extended structures?
Metallic elements have a unique property of forming extensive, elongated arrays where the atoms are arranged in a specific pattern throughout the solid. This arrangement is what gives metals their characteristic properties such as high electrical conductivity, malleability, and ductility. The repeating pattern of atoms in metals is known as a crystal lattice, and it is responsible for the strong bonding between metal atoms. The crystal lattice structure also allows metals to be easily shaped and molded into various forms, making them useful in a wide range of applications.
What is the crystal structure of a solid?
Crystals, also known as crystalline solids, possess unique internal structures that result in distinct flat surfaces or faces. These faces intersect at specific angles that are unique to the substance. Additionally, when subjected to x-rays, each structure produces a unique pattern that can be utilized to identify the material.
What is crystal structure explanation?
A crystal’s structure is determined by the way its atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in a repeating pattern. This internal arrangement is what defines the crystal’s structure, not its external appearance. In other words, the way the particles are organized within the crystal is what gives it its unique properties and characteristics. This is why crystallography is such an important field of study, as it allows us to understand the fundamental building blocks of matter and how they interact with each other.
By studying crystal structures, scientists can gain insights into everything from the properties of materials to the structure of proteins and other biological molecules.
What makes a crystal structure?
Crystal Structure is obtained by attaching atoms, groups of atoms or molecules. This structure occurs from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to produce symmetric patterns. A small group of a repeating pattern of the atomic structure is known as the unit cell of the structure.
Do all solids have crystal structures?
A crystal is a type of solid material that has a unique atomic arrangement that is periodic in nature. However, it’s important to note that not all solids are crystals. For instance, when water freezes, it starts with small ice crystals that eventually merge together to form a polycrystalline structure. It’s worth mentioning that quasicrystals are an exception to the rule, as they don’t have a periodic arrangement.
What solid has no crystal structure?
An amorphous solid is a type of solid material that lacks a specific lattice pattern in its atoms and molecules. This means that the structure of the material is not organized in a specific way, unlike crystalline solids. Examples of amorphous solids include plastic, glass, and gel. These materials are often used in various applications due to their unique properties, such as transparency, flexibility, and durability.
Despite their lack of a specific structure, amorphous solids can still exhibit interesting physical and chemical properties that make them useful in many industries.
What are the characteristics of a crystalline solid?
Crystalline solids are a type of material that possess unique properties. They are known for their firmness, as they hold a definite and fixed shape. Additionally, they are rigid and incompressible, meaning that they cannot be easily compressed or deformed. One of the defining characteristics of crystalline solids is their geometric shapes and flat faces, which can be observed in examples such as diamonds, metals, and salts.
To truly understand crystals, it is important to understand their structure and how it contributes to their properties.
What type of matter has a crystal structure?
Crystalline solids are composed of particles that are arranged in a highly organized structure, while amorphous or noncrystalline solids lack this ordered internal structure. There are several types of crystalline solids, including ionic solids, metallic solids, covalent network solids, and molecular solids. Each of these types has unique properties and characteristics that make them useful in various applications. Understanding the differences between these types of solids is important for scientists and engineers who work with materials on a regular basis.
What are examples of extended structures with two kinds of atoms?
Let’s shift our focus to the benefits of meditation for stress relief. If you’re an adult experiencing high levels of stress in your daily life, meditation can be a game-changer. Scientific research has shown that regular meditation practice can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being. One study found that mindfulness meditation can decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression, while another study showed that meditation can lower cortisol levels, the hormone associated with stress.
By taking just a few minutes each day to meditate, you can cultivate a sense of calm and inner peace that can help you better manage stress and improve your quality of life.
What are 5 examples of structures?
Load-bearing structures are all around us, from buildings and aircraft to anthills and beaver dams. These structures are essential components of our society’s infrastructure, providing support and stability for our daily lives. Construction results in two types of structures: buildings and non-building structures. Whether it’s a bridge or a salt dome, load-bearing structures play a crucial role in our world.
What would be an example of a structure?
A structure refers to an assemblage of multiple components that are combined to form a whole. It can take various forms, such as a towering skyscraper, a humble outhouse, the human body, or even a sentence.
Do metals have extended structures?
Metallic elements have a unique property of forming extensive, elongated arrays where the atoms are arranged in a specific pattern throughout the solid. This arrangement is what gives metals their characteristic properties such as high electrical conductivity, malleability, and ductility. The repeating pattern of atoms in metals is known as a crystal lattice, and it is responsible for the strong bonding between metal atoms. The crystal lattice structure also allows metals to be easily shaped and molded into various forms, making them useful in a wide range of applications.
Related Article
- Why Is A Bird Trying To Get In My House?
- Why I Want To Be On The Dance Team Essay?
- Why I Want To Be An Early Childhood Teacher Essay?
- Why I Want To Be A Critical Care Nurse Essay?
- Why I Want To Be A Chief Petty Officer Essay?
- Why I Sold My House And Moved Into An Apartment?
- Why Hasn’T My Ex Told Anyone We Broke Up?
- Why Has My Hamster Got A Lump On His Bum?
- Why Falling In Love Is Scary For A Strong Woman?
- Why Exploring The Ocean Is Mankind’S Next Giant Leap?