Have you ever wondered why brake lines in cars and trucks have so many bends and loops? It may seem like an unnecessary design, but in fact, these bends and loops serve a crucial purpose. They add flexibility to the brake lines, which is essential because vehicles bend and flex as they move. In the case of trucks, many have a frame that supports the body, and the brake lines need to be able to move with the frame. So, the next time you see all those twists and turns in your brake lines, remember that they are there for a reason.
Why do some brake lines have springs on them?
Armoured lines are a common feature in some steel brake lines. These lines are wrapped with coiled wire that resembles a spring. The primary purpose of this wire is to safeguard the brake line from rubbing against the chassis or body of the vehicle, which can cause damage and lead to brake failure. By using armoured lines, drivers can rest assured that their brake system is protected and functioning correctly, providing them with peace of mind while on the road.
Why can’t you use copper for brake lines?
Contrary to popular belief, copper brake lines are not more susceptible to electrochemical corrosion than steel ones. The concern about using copper in brake systems arises when discussing the possibility of electrochemical corrosion, which is a process that occurs between two dissimilar metals. However, this does not mean that copper brake lines are inherently more prone to corrosion than steel ones. In fact, copper is a highly durable and corrosion-resistant material that has been used in brake systems for many years with great success.
So, if you’re considering copper brake lines for your vehicle, rest assured that they are a reliable and safe option.
Is it OK to use copper brake lines?
“`Wondering if copper-nickel brake lines are legal? In the past, copper brake lines were banned due to their poor track record. However, with the introduction of copper-nickel brake lines, this product is now legal to use. Interestingly, the Copper Development Association now discourages the use of copper brake pads.“`
What is the difference between a brake line and a master cylinder?
The brake system’s pressure is determined by the master cylinder, while the brake lines simply transport the pressurized fluid. These lines are typically either 3/16 or 1/4 inch in diameter, and although there is no pressure variation between the two, the amount of fluid delivered will differ.
What happens if I don’t bench bleed master cylinder?
When it comes to replacing or installing a brake master cylinder, it’s important to remember the crucial step of bench bleeding. This process involves bleeding the cylinder before attaching it to the firewall, as the angle at which it sits can cause air bubbles to become trapped in the fluid passages if left un-bled. By taking the time to bench bleed your brake master cylinder, you can ensure that your brakes will function properly and safely.
Will master cylinder eventually bleed itself?
When filling the master cylinder, it’s important to note that it won’t automatically bleed the air out of the piston. This means that you’ll need to perform the bleeding process separately, outside of the vehicle. While it is possible to bleed the cylinder while it’s still in the car, this method is more time-consuming and requires two people – one to monitor for bubbles and another to press the brake pedal.
What happens if you get air in your master cylinder?
When you press the brake pedal, the pressure generated by the master cylinder travels through the brake line and applies force on the brake caliper and rotor. Unfortunately, if there are air bubbles in the brake line, the hydraulic pressure decreases, which can make your braking system less efficient and your vehicle harder to handle.
How do I know if my master cylinder needs bleeding?
If you’re checking your brake system, take a look at the fluid in the master-cylinder reservoir. If you see a lot of fluid bubbling up, that means there are still air bubbles in the system. You’ll need to bleed the brakes again to get rid of them. On the other hand, if the fluid is only slightly disturbed, that’s a good sign that your brake system has been properly bled.
What destroys master cylinder?
Over time, the internal and external seals of the brake master cylinder can become worn out. When the external seals are worn out, they can cause brake fluid to leak, which can lead to a reduction in the amount of fluid in the car and cause the brakes to malfunction. Additionally, if the fluid leaks into the brake booster, it can cause damage to it. It’s important to regularly check the condition of the seals and replace them if necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the brakes.
Why there are two holes in master cylinder?
The master cylinder has two ports that enable fluid to enter it: the fluid inlet port and the compensating port. The compensating port is located just ahead of the piston when it is at rest, while the fluid inlet port is situated just behind the lip that forms the front face of the piston.
What is the life expectancy of a master cylinder?
It’s important to note that, just like any other mechanical or hydraulic device, the master cylinder will eventually wear out. The lifespan of a master cylinder can vary depending on usage, with some lasting anywhere from 60,000 to 200,000 miles. For instance, highway commuters tend to use their brakes less frequently than city taxis, which means their master cylinders may last longer.
Can a master cylinder fail without leaking?
Yes master cylinders can fail without leakage, the clutch master cylinder has a piston inside and there are separate channels for hi-pressure line and return(low pressure) line and their location in the cylinder differs for manufacturers.
How do I test if my master cylinder is bad?
To test if your master cylinder is bad, start by checking the brake fluid level. If it’s low, add more and see if the problem persists. If the fluid level is fine, try pumping the brakes a few times to build up pressure. If the pedal sinks to the floor, it could be a sign of a bad master cylinder.
Another way to test is to apply pressure to the brake pedal and hold it for a few seconds. If the pedal slowly sinks to the floor, it’s likely that the master cylinder is failing. Additionally, if you notice any leaks or damage to the master cylinder, it’s best to have it inspected by a professional mechanic.
Why am I losing brake pressure but no leak?
Spongy brakes can be caused by various issues such as a brake line leak, a failed seal in the master cylinder, or air in the braking system. If you experience spongy brakes, the first thing you should do is quickly pump the brake pedal with your foot.
Why is my brake pedal spongy after bleeding?
If you’re experiencing a spongy brake lever or one that requires a long pull before the brakes engage, it’s likely that there’s air trapped in your brake system. Bleeding brakes can be a tricky process, and some brakes may be more difficult to bleed than others. In some cases, even after multiple attempts, air can still be trapped inside the caliper.
How do I know if I need a brake booster or master cylinder?
If you are experiencing issues with your brakes, it can be difficult to determine whether you need a brake booster or master cylinder. One way to tell is by checking the brake pedal. If it feels spongy or requires more pressure than usual to engage the brakes, it may be a sign of a failing master cylinder. On the other hand, if the pedal is hard to press and requires a lot of effort, it could indicate a problem with the brake booster.
It’s important to have your brakes inspected by a professional to accurately diagnose the issue and ensure your safety on the road.
Can you plug a brake line at master cylinder?
“`It’s not possible to connect the lines from the master cylinder to the rear brakes directly. This is because the master cylinder controls the left front and right rear brakes, as well as the right front and left rear brakes. To work on the rear brakes, you’ll need to clamp off the tubes located at the back of the vehicle.“`
What is another name for brake master cylinder?
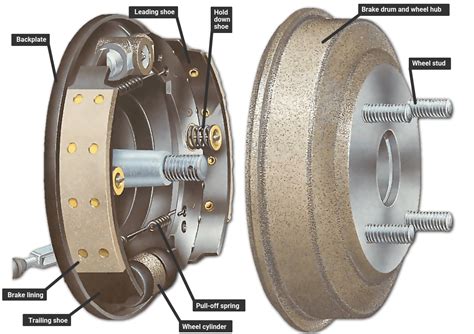
A hydraulic brake cylinder is a component of a vehicle’s braking system that converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is then used to activate the brake pads or shoes, which in turn apply friction to the wheels and slow down or stop the vehicle. Hydraulic brake cylinders are typically found in disc brake systems, where they are used to push the brake pads against the rotor, or in drum brake systems, where they push the brake shoes against the inside of the drum. Proper maintenance and regular inspection of the hydraulic brake cylinder is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of a vehicle’s braking system.
What are the two types of brake lines?
When it comes to passenger vehicle brake line flares, there are two main types to be aware of: the double flare (also referred to as the inverted flare) and the bubble flare (sometimes called the metric flare). It’s crucial to understand that these two types of flares cannot be used interchangeably. Each type has its own unique design and specifications, and using the wrong type of flare can result in brake failure and potentially dangerous situations. So, whether you’re repairing or replacing brake lines, make sure you know which type of flare is required for your specific vehicle.
Related Article
- Why Do Braces Take So Long?
- Why Do Braces Cost So Much?
- Why Do Boxers Hold Each Other?
- Why Do Box Turtles Dig Holes?
- Why Do Bowlers Tape Their Fingers?
- Why Do Bowlers Curve The Ball?
- Why Do Bottom Teeth Shift More?
- Why Do Bottom Teeth Get Crooked?
- Why Do Bottom Braces Hurt More?
- Why Do Borzois Have Long Noses?