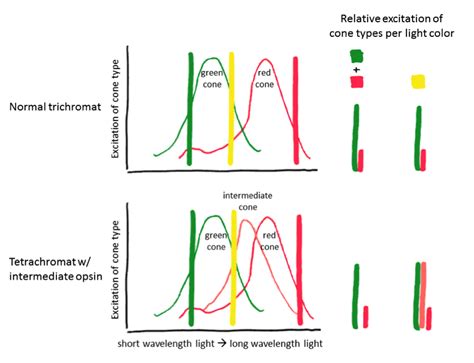
“`Tetrachromats are individuals with a rare genetic mutation that allows them to see more colors than the average person. However, some tetrachromats have reported feeling irritated by the color yellow. This is because their extra cone cells, which allow them to see more colors, are most sensitive to green and red light, but not yellow. As a result, yellow appears dull or muddy to them, causing discomfort.
Additionally, the brain may struggle to process the extra information from the additional cone cells, leading to sensory overload and further irritation. While tetrachromats have a unique ability to see a wider range of colors, it can also come with its own set of challenges.“`
Why do some people hate the color yellow?
It’s important to note that not everyone reacts to colors in the same way. What one person may find uplifting and cheerful, another may find irritating and unpleasant. Additionally, personal experiences and associations can greatly impact how a color is perceived. For example, while one person may associate a bright yellow with a sunny day at the beach, another may associate it with a negative experience.
It’s important to be mindful of these individual differences when using color in various contexts.
What color do tetrachromats see?
Did you know that some people have a fourth type of cone in their eyes that allows them to see more colors than the average person? These individuals are called tetrachromats and their unique photopigment enables them to perceive colors that are beyond the typical visible spectrum, which is commonly known as ROY G. BIV (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet). This means that tetrachromats can see a wider range of hues and shades, making their world more vibrant and colorful than most of us can imagine.
What is the psychology of the color yellow?
Yellow is a color that is often associated with positive emotions such as happiness, excitement, originality, enthusiasm, confidence, hope, and creativity. However, it can also be linked to negative feelings like cowardice, illness, caution, betrayal, egotism, and anxiety (“Yellow | Color Psychology”). It’s important to note that the interpretation of color psychology can vary from person to person and culture to culture. Nevertheless, understanding the potential emotional impact of colors can be helpful in various contexts, such as marketing, branding, and interior design.
What do tetrachromats see?
It’s fascinating to learn that tetrachromats have the ability to see colors that are beyond the range of most people. According to estimates, they can perceive up to 100 million colors, which is a hundred times more than the average human. This is because tetrachromats have an extra receptor in their retinas, which enables them to distinguish between subtle differences in color that others cannot. It’s amazing to think about how much more vibrant and nuanced the world must appear to them.
Can tetrachromats see UV light?
It’s fascinating to learn that some creatures, known as tetrachromats, possess four cells that enable them to see ultraviolet light. However, there are individuals who have a unique genetic condition that also grants them tetrachromacy. As a result, they can perceive an extensive range of colors that are not visible to the majority of people. It’s truly remarkable how our biology can impact our perception of the world around us.
How can I tell if I am a tetrachromat?
Did you know that the number of color receptors in your eyes can determine how many colors you can see? If you have three types of color receptors, you are a trichromat, which is the case for about half of the population. This means you can see between 20 and 32 colors. However, if you have four types of cones, you are a tetrachromat and can see between 33 and 39 colors. It’s fascinating to think about how our eyes and brains work together to perceive the world around us in different ways.
How many more colors can tetrachromats see?
It’s truly amazing to think that there are individuals who are born with four types of cones, a condition known as tetrachromacy. The term itself is derived from “tetra,” meaning four, and “chromacy,” which is related to color. With an extra cone, tetrachromats have an exponentially expanded palette-mixing ability, allowing them to see an estimated 10 to 100 million colors. It’s truly fascinating to consider the vast range of colors that exist in the world and how some individuals are able to perceive them in ways that most of us cannot.
Is tetrachromat a mutation?
Tetrachromacy is a rare genetic condition that affects only women, where they have four types of cones in their retina instead of the usual three. This means that they can see a wider range of colors and shades than the average person. While it is not a common condition, it is fascinating to think about how it could change the way someone experiences the world around them. Research is still ongoing to fully understand the implications of tetrachromacy and how it affects vision and perception.
What percentage of people are tetrachromat?
It’s interesting to note that only a small percentage, around 25 percent, of the population are tetrachromats. For those who may not know, tetrachromats are individuals who possess four types of cone cells in their eyes, allowing them to see a wider range of colors than the average person. In a recent test, there were 39 different colors presented, which some have criticized for not being comprehensive enough.
Which color is the most fatiguing color?
The most fatiguing color is believed to be yellow-green, also known as chartreuse. This color has a high level of brightness and can cause eye strain and fatigue when viewed for extended periods of time. However, the level of fatigue caused by a color can vary from person to person and can also depend on the context in which the color is being viewed. It’s important to take breaks and rest your eyes regularly when working with colors, especially bright or intense ones.
Additionally, incorporating calming colors like blue or green into your environment can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
What is the advantage of tetrachromacy?
Tetrachromacy is a fascinating condition that enables certain individuals to see colors that are beyond the range of most people’s perception. This occurs when an extra type of color receptor cell is present in the eye. Tetrachromats have the ability to distinguish an estimated 100 million color variations, which is an incredible feat. It’s amazing to think that some people have the ability to see a world of colors that most of us can only imagine.
How rare is it to have 4 cones in your eyes?
According to recent research, it has been estimated that around 12% of women possess four cone types, which is a rare genetic trait that allows them to see more colors than the average person. However, even if you have this trait, it is unlikely that you will ever know about it. Interestingly, if you have a father or son who is color blind, you are more likely to be tetrachromatic. Nonetheless, the ability to see more colors is still a fascinating phenomenon that continues to be studied by scientists.
What is the rarest eye feature?
It’s fascinating to learn that violet or red eyes are one of the rarest eye colors, with less than 0.01% of the population having this unique hue. Typically, this eye color is linked to albinism, a genetic condition that causes the absence of melanin, the pigment responsible for coloring hair, skin, and eyes. It’s interesting to note that while some people may find this eye color unusual, it’s still a beautiful and distinctive trait that sets individuals apart from the crowd.
What is the rarest eye form?
The rarest eye form is called the “central heterochromia.” This condition causes the iris to have different colors, with the inner part being a different color than the outer part. It is estimated that only 1% of the population has this unique eye color. Another rare eye condition is called “complete heterochromia,” where each eye has a different color.
This condition is also rare, with only 6 out of every 1,000 people having it. While these eye conditions may be rare, they are not harmful and do not affect vision. In fact, they can be quite beautiful and unique.
What is the rarest eyeball in the world?
According to some people, green eyes are the rarest eye color in the world. However, there are others who argue that green eyes have been surpassed in rarity by red, violet, and grey eyes.
Can humans see 10 million colors?
According to research, the average human can perceive approximately one million distinct colors. This is due to the fact that the human eye contains three types of cone cells, each capable of detecting roughly 100 different shades of color. As a result, the total number of possible color combinations that can be perceived by the human eye is estimated to be around one million.
What percentage of people are tetrachromats?
It’s interesting to note that only a small percentage, around 25 percent, of the population are tetrachromats. For those who may not know, tetrachromats are individuals who possess four types of cone cells in their eyes, allowing them to see a wider range of colors than the average person. In a recent test, there were 39 different colors presented, which some have criticized for not being comprehensive enough.
How is tetrachromacy described?
It’s truly amazing to think that there are individuals who are born with four types of cones, a condition known as tetrachromacy. The term itself is derived from “tetra,” meaning four, and “chromacy,” which is related to color. With an extra cone, tetrachromats have an exponentially increased ability to mix colors, allowing them to see an astonishing range of 10 to 100 million colors. It’s truly mind-boggling to imagine the richness and depth of the world that they experience.
Can you simulate tetrachromacy?
The latest research has discovered a fascinating method of tricking the brain into perceiving a fourth type of cone, which leads to tetrachromatic vision. This is achieved by wearing specially designed glasses that contain two types of filters. The researchers created two filters, one for each eye, to produce this effect. This breakthrough could have significant implications for the future of vision enhancement technology.
Related Article
- Why Are Tesla Tires So Expensive?
- Why Are Termites Attracted To Light?
- Why Are Tennis Skirts So Short?
- Why Are Tennis Lessons So Expensive?
- Why Are Tennis Bracelets So Expensive?
- Why Are Tennis Balls In Cans?
- Why Are Tempurpedic Mattresses So Expensive?
- Why Are Tempurpedic Beds So Expensive?
- Why Are Teddy Bears Never Hungry?
- Why Are Taro Chips So Expensive?