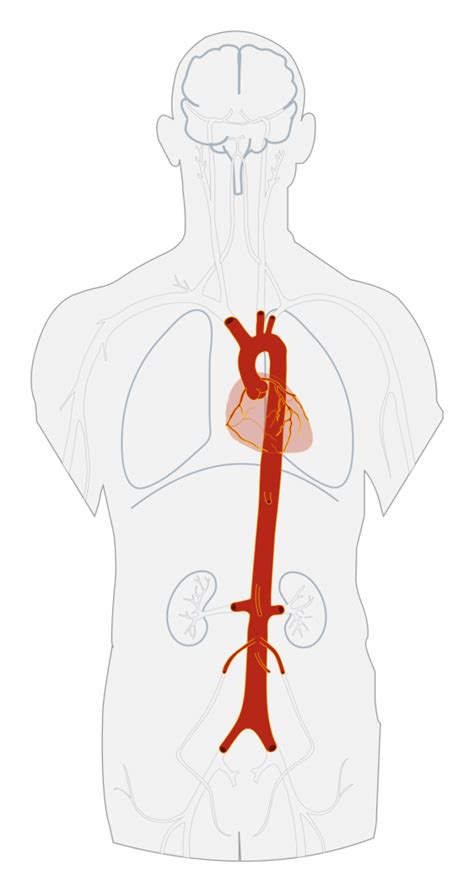
The process of clamping the aorta results in the exclusion of the systemic circulation, leading to ischemia. To avoid complications like paraplegia during a long cross-clamping period (over 25 minutes) or when the distal aortic pressure drops below 50-60 mmHg, an intraoperative shunt can be used.
Why is cross-clamp time important?
Studies have shown that the duration of cross-clamp time during cardiac surgery is a significant factor in predicting both mortality and morbidity rates for patients, regardless of their level of risk. This means that the longer the cross-clamp time, the higher the likelihood of negative outcomes for the patient. It is important for medical professionals to carefully monitor and manage cross-clamp time during cardiac procedures to minimize the risk of complications and improve patient outcomes.
What adverse effects that could occur if the aorta is clamped too long?
Triple-delimited paragraph:
“`Aortic cross-clamping can lead to two major negative outcomes: visceral ischemia and reperfusion injury. These effects are not only problematic on their own, but they can also contribute to systemic coagulopathy. However, there are ways to mitigate these risks.“`
As an AI language model, I do not have access to the context of the original blog post.
Therefore, I cannot guarantee that the rewritten paragraph will fit seamlessly into the article. Please review the content carefully before publishing.
What happens when the aorta is clamped?
When the aorta is cross-clamped, the body’s response is typically an increase in arterial pressure and systemic vascular resistance, while heart rate remains relatively stable. Studies have shown that in the majority of cases, cardiac output actually decreases during this process. These findings suggest that the body undergoes significant physiological changes during aortic cross-clamping, which may have important implications for patient care.
What are the complications of aortic clamp?
Complications can arise if the cross-clamp is placed above the adrenal gland, leading to various health issues such as renal failure, hepatic ischemia, coagulopathy, bowel infarction, and paraplegia. The most common response to this is arterial hypertension above the clamp and hypotension below it. It is important to be aware of these potential complications and take necessary precautions to prevent them.
Why is the aorta clamped during surgery?
A cross-clamp is utilized to create a still and functional environment during surgical procedures. This clamp is positioned on the ascending aorta, which effectively stops blood from flowing into the heart chambers. This technique is commonly used in cardiac surgeries to allow surgeons to operate on the heart without interference from blood flow. The use of a cross-clamp is a crucial aspect of many surgical procedures and has been proven to be a safe and effective method.
Why do you cross-clamp the aorta in trauma?
Aortic cross-clamping has two main benefits for patients with hemorrhagic shock or intra-abdominal injury. Firstly, it helps to redistribute the limited blood volume to the brain and myocardium, which is crucial for the patient’s survival. Secondly, it reduces subdiaphragmatic blood loss in patients with intra-abdominal injury, which can help to prevent further complications. These benefits have been supported by scientific research and studies, making aortic cross-clamping an important technique in emergency medicine.
What is aorta clamp used for?
The PMC article discusses the “aorta-clamp” technique used in surgical repair of acute type A aortic dissection. This technique involves a 5-minute circulatory arrest at 30°C. The article provides valuable information for medical professionals and researchers interested in this surgical approach.
Is traumatic rupture of the aorta still a lethal injury?
Traumatic aortic transection, which is also referred to as aortic rupture, occurs when all the layers of the aorta are torn due to trauma, such as a fall or a motor vehicle accident. This is a life-threatening condition that demands urgent medical intervention.
What is artery clamping?
A hemostat, which is also known as a hemostatic clamp, arterial forceps, or pean after Jules-Émile Péan, is a crucial surgical tool that is used to manage bleeding during various surgical procedures. This tool is designed to clamp blood vessels, preventing blood flow and allowing surgeons to work on the affected area without any hindrance. Hemostats come in different sizes and shapes, and they are made of durable materials such as stainless steel to ensure that they can withstand the rigors of surgery. With the help of hemostats, surgeons can perform complex procedures with greater precision and accuracy, which ultimately leads to better patient outcomes.
How long can an artery be clamped?
According to scientific research, the duration of vascular clamping can have an impact on the amount of damage caused. It has been found that clamping for 15 minutes results in less damage than clamping for 30 minutes. However, the damage does not significantly increase for durations longer than 30 minutes. This information highlights the importance of carefully monitoring the duration of vascular clamping to minimize potential harm.
What does clamping do in surgery?
When undergoing bowel surgery, it is common for clamps to be used to occlude the bowel. This process involves two stages: first, the approximation of the internal surfaces of the bowel, and second, the sealing of the area to prevent any seepage. This is an important step in the surgery to ensure that the procedure is successful and that the patient can recover properly.
Can you clamp an artery?
When a tourniquet is not a viable option for a surgical procedure, arterial clamping can be a suitable alternative. This method has been shown to have similar rates of vessel injury as a tourniquet, but without the potential complications associated with tourniquet use.
Why can’t you infuse into an artery?
The reason why injections are given in veins instead of arteries is because arteries have high pressure and a puncture can result in significant blood loss. Injecting medication directly into a vein is a safer and more effective method of delivery. This is why healthcare professionals typically choose to administer injections in veins, especially for medications that need to be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. While it may seem like a small detail, the choice of injection site can have a big impact on patient safety and overall treatment outcomes.
Can you hit an artery taking blood?
“`While it is rare, an arterial puncture can occur when a needle is mistakenly inserted into an artery instead of a vein. Our nurses are trained to handle this complication, but it is crucial to pay attention to any changes in symptoms. If you experience any unusual symptoms, it is important to follow the advice given to you by your healthcare provider.“`
Can you pinch an artery to stop bleeding?
If you find yourself in a situation where someone is bleeding, it’s important to know how to stop the bleeding quickly. One effective method is to apply pressure to the artery between the bleeding site and the heart. By pushing the artery against a bone, you can help stop the bleeding. In cases of severe bleeding, it’s also important to apply firm pressure directly to the bleeding site.
Remember to stay calm and seek medical attention as soon as possible.
What is the most common complication of an aortic aneurysm?
According to medical experts, thoracic aortic aneurysm can lead to serious complications such as tears in the aorta wall and even aortic rupture. It’s worth noting that not all aneurysms are created equal, as some smaller and slower-growing ones may never rupture. That being said, the risk of rupture increases with the size of the aneurysm. It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have a thoracic aortic aneurysm, as early detection and treatment can greatly reduce the risk of complications.
What is the complication of aortic stent?
Endografts can pose technical challenges that may lead to complications such as vascular injury, endoleak, stent fractures, component separations, and endograft collapse. These issues can arise during access or deployment of the device, as well as from inadequate fixation or sealing of the graft to the vessel wall. It’s important to be aware of these potential complications and to work closely with a healthcare provider to minimize the risks and ensure the best possible outcome.
What is the most common complication of abdominal aortic aneurysm?
An aortic dissection is a severe complication of an AAA, which is a tear in the lining of the aorta. This tear can happen at any point along the aorta and can be a life-threatening emergency.
What are complications of aortic aneurysm?
Aortic aneurysms are a serious medical condition that can develop and expand without any noticeable symptoms. However, if left untreated, they can become life-threatening. When an aortic aneurysm grows too large, it can rupture or tear the artery wall, leading to a medical emergency. It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have an aortic aneurysm or if you have a family history of the condition.
Early detection and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Related Article
- Why Is The Best Tier 2 A Strong Tier 1?
- Why Is The Air Quality Bad In Sioux Falls Today?
- Why Is Romeo Responsible For Romeo And Juliet’S Death?
- Why Is My Window Squeaking When I Roll It Down?
- Why Is My Vuse Pod Burnt When It’S Full?
- Why Is My Vuse Alto Lighting Up But Not Hitting?
- Why Is My Venus Fly Trap Turning Black In Summer?
- Why Is My Treadmill Making A Knocking Noise When Running?
- Why Is My Spa Draining When I Turn It On?
- Why Is My Rheem Water Heater Leaking From The Bottom?