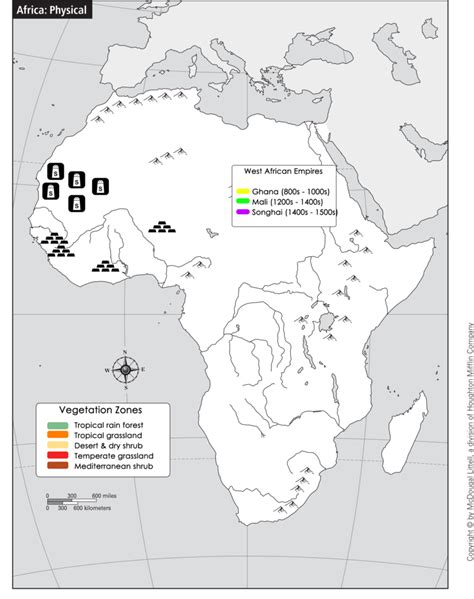
West Africa flourished with the establishment of numerous prosperous trading empires. These kingdoms owed their wealth and influence primarily to the extensive trade conducted along the trans-Saharan trade routes. Given the vital role trade played in their survival, the leaders of these kingdoms actively promoted and facilitated trade, providing unwavering support to merchants and their activities.
Why were the West African kingdoms so prosperous?
Ghana’s rulers amassed immense wealth through trade, levies imposed on traders and the citizens of Ghana, as well as their personal reserves of gold. This wealth was utilized to establish a formidable army and expand their empire. The extensive trade networks facilitated interactions between the people of Ghana and individuals from diverse cultures and belief systems.
What was West Africa’s most prosperous kingdom?
West Africa’s most prosperous kingdom was the Kingdom of Ghana. It emerged around the 6th century and reached its peak between the 9th and 11th centuries. Ghana’s wealth was primarily derived from its control over the trans-Saharan trade routes, particularly the trade of gold and salt. The kingdom’s location allowed it to monopolize the trade of these valuable commodities, leading to immense wealth and power.
Ghana’s rulers, known as the Ghana kings, taxed the trade and accumulated vast amounts of gold, which further enhanced their prosperity. The kingdom’s prosperity attracted merchants from North Africa and the Middle East, who sought to engage in lucrative trade with Ghana. However, the kingdom eventually declined due to internal conflicts and invasions from neighboring empires.
How did the African empires get so wealthy?
The Yoruba empire, founded in the 15th century, was a significant West African state known for its impressive size and influence. This empire thrived due to its prosperous trade and the formidable strength of its cavalry.
What is the main reason the three West African kingdoms were successful?
Scholar-Griot: Rebecca Allyson Schnabel, M.S. During the medieval period in Europe, knights were known for their gallant adventures. However, it is important to recognize that while these knights were riding around, the three great empires of West Africa – Ghana, Mali, and Songhai – were flourishing with immense wealth.
In fact, these empires possessed more gold and engaged in more global trade than any European power of that era. This historical fact sheds light on the remarkable achievements and influence of West African civilizations during this time.
What were two ways of earning a living in a West African kingdom?
Although West Africans were primarily engaged in agriculture, they also had a diverse range of occupations. Among them were hunters and fishers, who relied on the abundant natural resources in the region. Additionally, merchants played a crucial role in trading with other African communities, as well as with Europeans and Arabs, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. Furthermore, some West Africans were involved in mining activities, extracting valuable resources such as gold, salt, iron, copper, and even diamonds.
This multifaceted economy allowed for a variety of livelihoods and contributed to the overall prosperity of the region.
What factor was most important in the three West African kingdoms growth in power?
Trade played a significant role in the growth and prosperity of West African kingdoms. Ghana, Mali, and Songhai were powerful entities that controlled vast territories and were known for their prowess in trade. These kingdoms are often referred to as both empires and kingdoms by historians due to their extensive influence.
How did the West African empires grow in strength?
They achieved dominance by monopolizing the gold and salt trades. These three empires maintained control over the Sahel region of West Africa for a remarkable span of 900 years. Additionally, various trading kingdoms emerged in Africa, thriving on commerce. Some specialized in gold trade, while others dealt in valuable commodities like ivory and leopard skins.
What are two factors that led to the growth and rise of West African empires?
Geography played a crucial role in shaping the West African societies, particularly in terms of trade. Waterways served as vital channels for transporting goods that were to be exchanged. Not only did these societies benefit from the trade itself, but their rulers also imposed taxes on the items that entered or left their empires. This allowed them to generate additional revenue and maintain control over the economic activities within their territories.
What played the biggest role in the growth of West African empires?
The Ghana Empire experienced a significant boost in wealth and influence due to the rapid expansion of trade in West Africa. This growth was particularly fueled by the trans-Sahara trade, which brought immense prosperity to the empire. One of the key factors contributing to their success was their control over the three major gold fields located to the south of their territory. This advantageous position allowed the Ghana Empire to accumulate substantial wealth and solidify their power in the region.
How did the West African empires grow and develop?
West Africa flourished with the establishment of numerous prosperous trading empires. These kingdoms owed their wealth and influence primarily to the extensive trade conducted along the trans-Saharan trade routes. Given the vital role trade played in their survival, the leaders of these kingdoms actively promoted and facilitated trade, providing unwavering support to merchants and their activities.
What did all West African empires have in common?
All three Western African kingdoms relied heavily on the trade of gold and salt, as well as their control over the Niger River, in order to establish their dominance in West Africa.
What was the economy of the West African empire?
The trade in West Africa primarily revolved around valuable commodities like gold and salt. These resources brought immense prosperity to powerful empires like Ghana and Mali. Additionally, there were other goods that were frequently exchanged, such as ivory, kola nuts, cloth, slaves, metal goods, and beads.
Which were the important West African empires?
The Middle Ages in West Africa witnessed a fierce competition among three powerful kingdoms for dominance over the trans-Saharan trade routes. These kingdoms were the Ghana Kingdom, the Mali Kingdom, and the Songhay Kingdom.
What is West Africa known for?
West Africa boasts a diverse and vibrant ecology, characterized by its abundant biodiversity and unique geographical regions. The climate and ecology of this area are greatly shaped by its surrounding natural features. To the north and east, the dry Sahara desert exerts its influence, bringing in dry winds during the Harmattan season. On the other hand, the Atlantic Ocean to the south and west contributes to the region’s climate through seasonal monsoons.
This combination of factors creates a dynamic and ever-changing environment in West Africa.
Why was the West African civilization important?
A mutually beneficial trade had emerged in West Africa, where they exported valuable commodities like gold, cotton cloth, metal ornaments, and leather goods through the trans-Saharan trade routes. In return, they received copper, horses, salt, textiles, and beads. As time went on, the trade expanded to include ivory, slaves, and kola nuts as well. This trade played a significant role in the economic development of the region.
What are 3 characteristics of West Africa?
Dry, desert conditions exist to the north and tropical conditions exist to the south. The main economic activity in the region is subsistence agriculture. Minerals, diamonds, or oil are also extracted in varying amounts in West Africa.
What is unique about West African culture?
The West African culture is rich in various aspects, one of which is its oral traditions. These traditions encompass a wide range of practices, including the sharing of folktales. Folktales are stories that are passed down through generations by word of mouth. They serve as a means of entertainment, education, and cultural preservation.
One popular type of folktale found in West Africa is the trickster folktale. These stories often revolve around an animal or human character who uses their wit and cunning to outsmart others. One well-known example of a trickster folktale is the story of Brer Rabbit. Through these tales, West African communities have been able to pass down important lessons and values from one generation to the next.
What are the three major West African kingdoms and what was their wealth based on?
The West African Trading Empires of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai were incredibly influential and prosperous states during their respective time periods. Ghana thrived from 800 to 1050 CE, followed by Mali from 1235 to 1464 CE, and finally Songhai from 1464 to 1591 CE. These empires held significant control over the lucrative gold and salt trade in West Africa. One of the key factors contributing to their success was the strategic positioning of their cities at the crossroads of major trade routes.
This allowed them to establish and maintain a strong grip on the flow of goods and resources throughout the region.
Why were West African kingdoms like Ghana and Mali successful?
Why were West African kingdoms like Ghana and Mali successful during the Post-Classical period? One of the key reasons for their success was their establishment of trade relations with Muslims and their adoption of the religion of Islam. This allowed them to tap into the vast networks of trade and commerce that spanned across the Islamic world, opening up new opportunities for economic growth and cultural exchange. Additionally, the adoption of Islam brought about significant political changes within these kingdoms. The rulers of Ghana and Mali embraced Islam, which not only provided them with a religious identity but also helped to legitimize their rule and strengthen their political authority.
This religious conversion also facilitated diplomatic relations with other Muslim states, further enhancing their political standing on the international stage. Overall, the trade relations with Muslims and the adoption of Islam played a crucial role in the success of West African kingdoms like Ghana and Mali during the Post-Classical period.
What became the largest of West Africa’s three trading kingdoms?
8. One of the most influential and prosperous trading states in West Africa was Mali, which was founded in the mid-1200s by Sundiata Keita. Mali’s territory stretched from the Atlantic coast all the way to the renowned trading hub of Timbuktu. The wealth and strength of Mali were primarily derived from the lucrative gold-salt trade.
Among the notable rulers of Mali, Mansa Musa stood out as one of the wealthiest and most powerful kings in history.
What did the three great West African kingdoms have in common?
All three Western African kingdoms relied heavily on the trade of gold and salt, as well as their control over the Niger River, in order to establish their dominance in West Africa.
Related Article
- Why Were The Seven Deacons Chosen?
- Why Were The Levites Set Apart?
- Why Were Political Machines Effective Apex?
- Why Wear White To A Funeral?
- Why We Were Chosen Alcoholics Anonymous?
- Why We Were Chosen Aa Pdf?
- Why We Sleep Audiobook Free Download?
- Why Water Heater Keeps Turning Off?
- Why Wasnt Audrey In Descendants 2?
- Why Was Zombie House Flipping Cancelled?